Earthing System
Earthing, also known as grounding, is a fundamental concept in electrical engineering and safety. It involves establishing a direct connection between electrical devices, systems, or structures and the Earth’s conductive surface. The primary purpose of earthing is to provide a safe path for electrical currents to flow to the ground in the event of a fault or malfunction, thereby preventing electric shock hazards and protecting equipment from damage.
There are several key aspects to understanding earthing:
1. Safety: Earthing is crucial for ensuring the safety of individuals working with or around electrical systems. By providing a low-resistance path to the ground, earthing helps to dissipate excess electrical energy and prevent the buildup of dangerous voltages that could lead to electric shock.
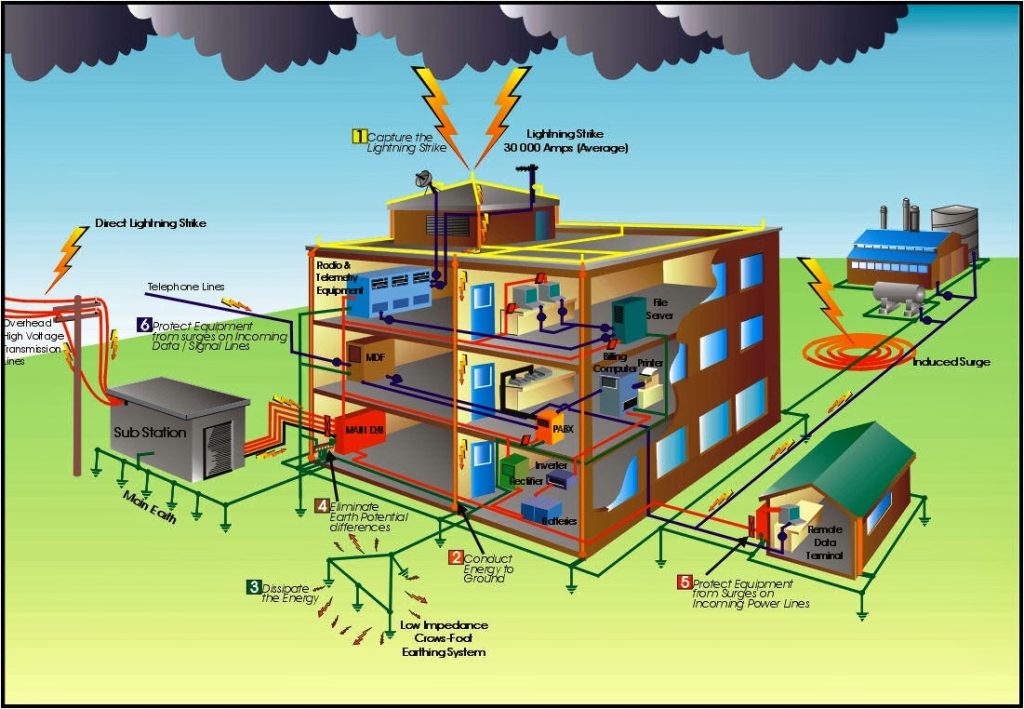
2. Equipment Protection: In addition to safeguarding human life, earthing also protects electrical equipment and devices from damage caused by transient voltage surges, lightning strikes, or short circuits. By directing fault currents away from sensitive components, earthing helps to minimize the risk of equipment failure and prolong the lifespan of electrical systems.
3. Functional Requirements: Earthing systems are designed to meet specific functional requirements, including maintaining the electrical potential of conductive surfaces, minimizing electromagnetic interference, and ensuring the proper operation of protective devices such as circuit breakers and fuses.
4. Types of Earthing: There are various methods of earthing, depending on the specific application and requirements. Common types of earthing systems include:
5. Single-point earthing: A single connection point is established between the electrical system and the ground.
6. Multiple-point earthing: Multiple connection points are distributed throughout the electrical system to ensure uniform grounding.
7. Plate earthing: A large metal plate buried in the ground serves as the earthing electrode.
8. Rod earthing: A metal rod or electrode is driven into the ground to provide a connection for the electrical system.
Earthing Standards and Regulations: Governments and industry organizations establish standards and regulations governing the design, installation, and maintenance of earthing systems to ensure compliance with safety requirements and best practices. These standards typically address factors such as soil resistivity, electrode placement, bonding requirements, and testing procedures.
Overall, earthing is a critical aspect of electrical safety and system reliability, playing a vital role in protecting both people and equipment from the potentially harmful effects of electrical faults and disturbances. Understanding the principles and practices of earthing is essential for anyone involved in the design, installation, or maintenance of electrical systems.